Harvesting
Light Energy
-
Photosynthesis -

The process of
photosynthesis is the major gateway for the energy that moves into the
ecosystems of our planet. The process converts light energy from the sun
into chemical energy in the form of building covalent bonds within organic
molecules (mostly). As you may realize this chemical energy (in the form
of organic molecules) can be used in cellular respiration. Virtually ALL
life forms on our planet depend directly or indirectly on photosynthesis
(there are exceptions). Photosynthetic bacteria, algae as well as plants
are organisms able to perform photosynthesis. Many non-photosynthetic lifeforms
have established relationships with photosynthetic partners. [Do
not get too bogged down in the details of this section.]
-
Why do we discuss photosynthesis
in our class?
-
What is accomplished by the process
of photosynthesis?
-
What kind of organisms perform
photosynthesis? Give examples?
-
These lifeforms are often referred
to as producers? Why?
-
Can animals photosynthesize? Do
they depend on photosynthesis?
-
Coral reefs are produced by animals
and depend on light energy. Why is that?
-
What is the overall formula of
photosynthesis? Describe the reactants and the products.
-
In which organelle does this process
take place in algae and plants? In photosynthetic bacteria? In animals?
-
Describe the structure of the
chloroplast. Name the different parts? Which lifeforms have chloroplasts?
-
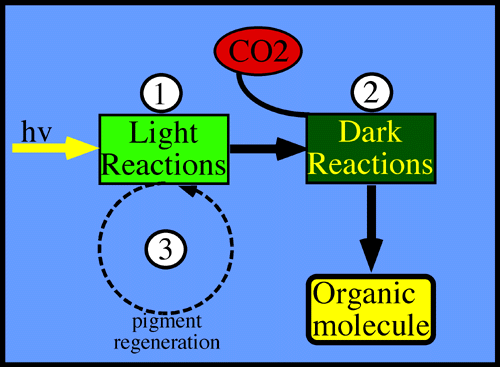
What is the difference betweem
the light- and the dark reactions? What is accomplished by each?
-
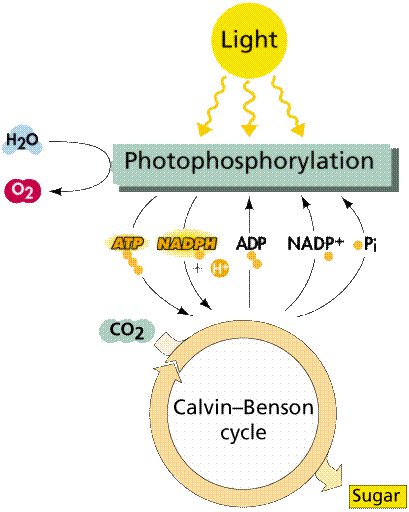
How does photosynthesis produce
sugars? What happens to any excess of sugars produced during photosynthesis?
-
Where does oxygen come from?
-
What is the role of the different
pigments used in photosynthesis?
-
What kind of light does chlorophyll
absorb?
-
Why are most plants green?
-
Are there other pigments than
chlorophyll? What is the purpose of these pigments?
-
Understand how light is a form
of energy. Relate visible light to the electromagnetic spectrum. Again,
what is the role of pigments in photosynthesis?
-
Try to summarize (again) what
is accomplished in the two processes (light reactions versus the Calvin
Cycle). How do they depend upon each other? What is produced? What goes
into the cycles?
This simplistic overview gives
you an idea about the two main pathways of photosynthesis. What is accomplished
in each of them? To the right is a more detailed overview incorporating
the major energy carrying molecules involved. [Note: the dark reactions
are often referred to as the Calvin Cycle after its discovererers].
-
What is the ecological and evolutiuonary
importance of photosynthesis in biological systems?
Links:
-
Biology
Book - Photosynthesis: An excellent overview
of photosynthesis with lots of graphics. The page may take a while to load
unless you have a fast connection, but it is definitely worth the wait.