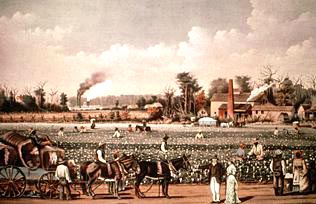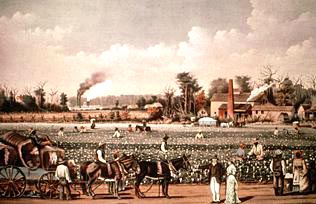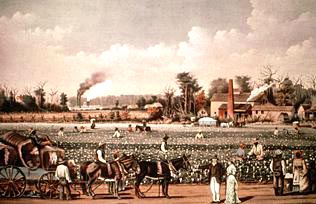
United States History 17A
Study Guide 10
 Assignments
Page
Assignments
Page
 Previous
/Next Study Guide
Previous
/Next Study Guide
 Today
in U. S. History
Today
in U. S. History

Study Guide 10
Nation of Nations
Chapter Thirteen
The Old South
Answer the following questions:
1. Why could cotton, rice and sugar be grown only
in
the
south?
I. The Social Structure of the Cotton Kingdom.
2. What was the 'black belt' region of Alabama,
and
what
opened up this area for agriculture?
3. What area, even farther west, attracted cotton
planters?
By the time of the Civil War, what percent of the total cotton crop
came
from west of the Mississippi River?
4. What crop was 'king' in the
south -- the major source of wealth?
By 1860,
75 percent of the world's ____ came from the United States?
5. What were two problems created by reliance on
a
single
crop?
6. What was perhaps the most striking
environmental
consequence
of the expansion of southern society? Where was one particularly
notorious
area?
7. As cotton transformed the boom country of the
Deep
South,
what became the major crops (not the staple crops) of the upper south?
Because these crops required less labor, what happened to the surplus
of
slaves in the upper south?
8. What was the price of a prime field hand in
the
Deep South
by the late 1850s? Why was this so much higher than in the early 1840s?
9. By 1860, what percent of the labor force north
and
south
was engaged in agriculture?
10. In the years before the Civil War, what
percent
of the
nation's manufactured goods came from the south? Why did so few
cities
develop in the south?
11. Why were free public schools rare in the
south?
In 1850,
what percent of native-born, white southerners were unable to read and
write? How does this compare to the rate for New England?
12. Compared to land, how much were all the
slaves
worth?
13. How much per year did the average slaveowner
spend to
support an adult slave? How much could a planter expect a slave to
produce
in cotton? Thus, a slaveowner took about ___ percent of the weatlh
produced
by a slave's labor.
II. Class Structure of the White
South
14. In 1860, what percent of the 8 million white
southerners
either owned slaves or were members of slave-owning families? How many
white southerners belonged to families of the planter class, that is,
those
who owned of 20 or more slaves? What percent of all slaves did the
planter
class own? What percent of the region's total wealth did they control?
15. How large was the typical plantation? How
many
slaves
lived and worked there? Why weren't they larger? How did the larger
slaveowners
handle this problem?
16. Where was the legendary 'Old South' located?
What
was
the ideal of this area?
17. In what 3 ways did the cotton lords of
Alabama
and Mississippi
differ basically from the Tidewater planters?
18. Identify five tasks that a plantation master
had
to coordinate.
19. How did planters often seek to expand their
production?
20. Where did some of the most brutal forms of
slavery exist?
Why?
21. What were five of the responsibilites of the
plantation
mistress?
22. What did some of these plantation mistresses
find confining about their lives?
23. What were the penalties for southern men who
fathered
illegitimate children by slave women? What were the penalties for men
who
raped slave women? What was the penalty for white women who were guilty
of adultery?
24. Who accounted for over one-half of the
southern
white
population? How many slaves and how much land did they own?
25. For what 3 reasons could these people not
compete
with
planters in the production of staples?
26. Why did the yeoman farmers admire the
planters
and why
did they accept slavery?
27. Where did the poorest white southerners live?
About what
percent of the population did they represent? What were their lives
like? Why did poor whites favor slavery?
III. The Peculiar Institution
28. On what 2 types of farms might slaves
generally
be found?
How were they supervised on each? Which plantations required the
longest
hours and the most grueling labor?
29. Which slaves were accorded the highest satus?
30. On large plantations, what were the 'gang'
and
'task'
systems? Which system was preferred in the rice fields? In the cotton
fields?
31. What time did work begin and end for most
slaves?
How
long might they work during times of cultivation and harvest? Did this
include Saturdays and Sundays?
32. In what four ways might slaves be punished by
their masters?
What was the most common way?
33. How, most commonly, were slaves housed? On
average, how
much did a planter spend per year on medical care for each slave? Fewer
than __ of slave children lived to the age of 10. For those slave
children who survived past the age of 10, what was their life
expectancy compared to white Americans?
34. For what 4 reasons were slave revolts more
rare
in the
United States that in Latin America?
35. Apart from revolts, what were four more
subtle
ways of
resistance among slaves? What was the most common form of
resistance?
IV. Slave Culture
36. What was one of the most remarkable
achievements
of African-Americans
in bondage?
37. Why were songs so important among slaves?
38. What kind of family was the rule among slaves?
39. In what 3 ways did masters control religion
among
slaves?
40. What was a 'hush harbor'?
41. From religion, slaves learned that God would
___
and
raise ___ . Slave preachers assured their congregations that ___ ?
42. In the years before the Civil War, how many
calories
per day did the average adult slave receive? From what sources mostly?
What were the results? What was a hoecake?
V. Southern Society and the Defense of Slavery?
43. Of the 4 milliion African Americans living in
the
south
in 1860, what percent were free?
44. Following Nat Turner's rebellion in 1831,
what
were 7
ways that southern legislatures restricted the behavior of free African
Americans?
45. In what five ways did the south justify
slavery?
Whom
were the defenders of slavery expecting to influence with these
apologies
for slavery? Why?
Please click on the site, The
Confessions of Nat Turner, read the selections there, and answer
the
following questions:
46. For what did Nat Turner believe he was
intended?
What
motivates Nat Turner?
47. What sign appeared to Turner, after which he
prepared
himself to slay his enemies? Why?
48. What happens to Nat Turner?
49. According to the 'Recollections of Harriet
Jacobs', after
Nat Turner's insurrection began, what did the country bullies and poor
whites do? What stopped them?
Please click on the site, The
Wonderful Tar Baby, read the selection there, and answer the
following
questions:
50. Why does Brer Fox put the tar baby in the
road?
Why does
Brer Rabbit get stuck in it? How does Brer Rabbit get out of his
predicament?

 Assignments
Page
Assignments
Page
 Revised April 7,
2008
Revised April 7,
2008
by Tom Gallup, e-mail address: [email protected]
West Valley College
http://www.westvalley.edu/wvc/ss/gallup/gallup.html